Understanding and Treating Ingrown Toenails: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction:
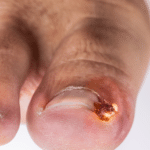
Ingrown toenails are a common, yet often painful condition that occurs when the edge of a toenail grows into the surrounding skin. While it may seem like a minor issue, if left untreated, ingrown toenails can lead to infection and further complications. Fortunately, there are several effective treatments available to alleviate the discomfort and prevent recurrence. In this guide, we’ll delve into the causes, symptoms, and various treatment options for ingrown toenails.
Understanding Ingrown Toenails:
To understand ingrown toenails, it’s essential to know their causes.
1. **Improper Nail Trimming:** Cutting toenails too short or rounding the edges instead of trimming straight across can increase the risk of ingrown toenails. When nails are trimmed too short, the skin may grow over the nail, causing it to become ingrown.
2. **Ill-Fitting Footwear:** Wearing shoes that are too tight or narrow can exert pressure on the toes, pushing the skin into the edges of the toenails. This pressure can cause the nails to grow into the skin and lead to ingrown toenails.
3. **Toe Trauma:** Injuries to the toes, such as stubbing or jamming, can damage the nail matrix or surrounding tissue, increasing the likelihood of ingrown toenails.
4. **Genetics:** Some people may be genetically predisposed to developing ingrown toenails. Factors such as the shape and structure of the toenails, foot anatomy, and inherited conditions can contribute to the risk of ingrown nails.
5. **Abnormal Nail Growth:** Certain nail conditions, such as thickened or curved nails, can make ingrown toenails more likely to occur. Conditions like fungal infections or nail dystrophies can alter the shape and texture of the nails, making them more prone to becoming ingrown.
6. **Excessive Sweating:** Profuse sweating in the feet can soften the skin and make it more prone to irritation and infection. Moist environments also facilitate bacterial and fungal growth, increasing the risk of ingrown toenails.
7. **Poor Foot Hygiene:** Inadequate foot care, such as neglecting to clean and dry the feet properly, can create an environment conducive to bacterial and fungal infections. These infections can contribute to inflammation and ingrown toenails.
8. **Chronic Health Conditions:** Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes or peripheral vascular disease, can impair circulation to the feet and affect nail health. Individuals with these conditions may be at a higher risk of developing ingrown toenails and experiencing complications.
9. **Heredity:** Some individuals may inherit a predisposition to ingrown toenails from their parents. Factors such as the shape and structure of the toenails can be passed down through genetics, increasing the likelihood of ingrown nails.
Symptoms of Ingrown Toenails:
Recognizing the symptoms of ingrown toenails is crucial for prompt treatment. Common signs include:
1. Pain and tenderness along the sides of the toenail.
2. Redness and swelling around the affected area.
3. Difficulty wearing shoes due to pressure on the toenail.
4. Formation of pus or drainage if infection is present.
5. Overgrowth of skin around the toenail.
Treatment Options:
The treatment for ingrown toenails varies depending on the severity of the condition. Mild cases may be managed at home, while more advanced cases may require professional intervention. Here are some common treatment options:
1. **Professional Treatment:**
– Your physician may elect to proceed with a nail avulsion vs a matrixectomy
– Antibiotics: If an infection is present, your doctor may prescribe oral antibiotics to clear the infection.
2. **Preventive Measures:**
– Trim toenails straight across and avoid cutting them too short.
– Wear properly fitting shoes with adequate toe room.
– Maintain good foot hygiene and keep feet clean and dry.
– Avoid picking or tearing at toenails, as this can lead to ingrown nails.
Conclusion:
Ingrown toenails can be a source of significant discomfort and inconvenience, but with proper treatment and preventive measures, they can be effectively managed. Whether through at-home remedies or professional intervention, it’s essential to address ingrown toenails promptly to prevent complications and promote healing. If you’re experiencing persistent pain or signs of infection, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional for personalized treatment recommendations. Your feet will thank you for it!
